Abstract
Introduction:CD20 a cell surface protein selectively expressed in mature B cells is involved in regulation of B cell differentiation and is a well-established target for anti-CD20 therapy in the treatment of B cell malignancies. However, therapeutic resistance to anti-CD20 antibodies, including rituximab and obinutuzumab, continues to remain a major obstacle in the treatment for NHL patients. Known mechanisms of anti-CD20 resistance include loss of CD20 expression, apoptotic dysfunction and/or poor immunoreactivity. Further mechanisms, including potential biologic etiologies, which engender resistance to anti-CD20 antibodies remain largely unclear. We sought to delineate the immuno-biological landscape and mechanisms associated with anti-CD20 resistance via systems biology analyses and immune functional studies with rituximab and obinutuzumab resistant (RR & OR) NHL models in a novel single-cell microfluidics platform.
Methods:RR or OR cells (SUDHL4 and SUDHL10) were developed by repeated culturing with chronic low dose exposure to antibody (Ab) drugs. Anti-CD20 resistance was biologically characterized by CD20 immunostaining-flow cytometry, gene expression profiling and systems biology analysis (with Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA). Immunological characterization was performed using NK mediated ADCC activity (AcellaTox-Glo), real-time analysis of NK cell-NHL interaction kinetics by microfluidics and cytokine/immune factor secretion using proximity extension assay (Olink immuno-oncology panel). Ionomycin induced release of Calcium assay was performed using Fluo-4 cell-based assay and plate reader.
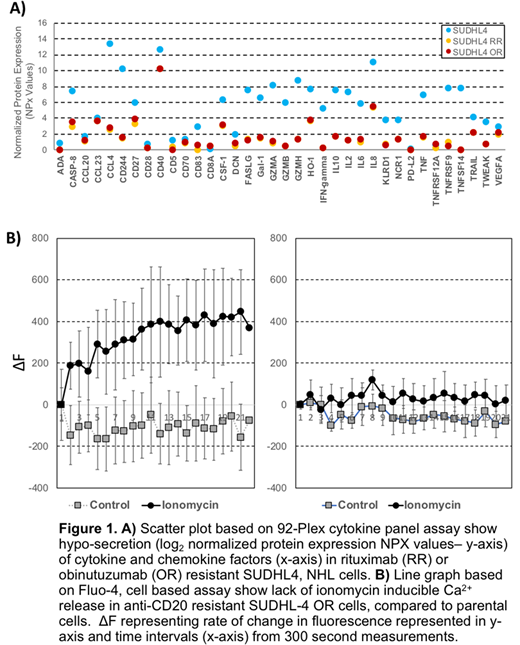
Results: Flow cytometric studies and ADCC assays using anti-CD20 Abs and primary NK cells, exhibited prominent downregulation of CD20 cell surface expression and markedly decreased NK mediated ADCC activity in RR (11%, P=0.0002) and OR (17%, P=0.001) compared with 10mg/ml of rituximab (51%) or obinutuzumab (56%), respectively, in the parental SUDHL4 cells. The basal NK mediated Furthermore, microfluidic analyses revealed decreased cell-cell interactions among NK cells and anti-CD20 resistant NHL cells in the presence of either antibody. Systems biology analysis of the transcriptome with these RR and OR cells showed downregulation of immune signaling mechanisms closely related MAPK, NFkB, mTOR and JAK/STAT pathways, with partial upregulation of PLCγ, B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling (via western blot). Using the Olink 92-plex cytokine assay, we observed hyposecretion of the majority of cytokines including IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, TNFα, IFNγ and FASL all CD20 resistant cells (Fig. 1A). Based in part on these biological changes, we hypothesized that loss of CD20 associated with decreased calcium signaling could be the master regulator observed with anti-CD20 resistance. Assessment of ionomycin-induced releasable calcium showed lack of ionomycin releasable calcium in anti-CD20 resistant cells (Fig. 1B). Treatment with the depolarizing agent, veratridine, restored ionomycin releasable calcium levels, reversed BCR signaling, and it was accompanied with significantly decreased cell viability (60%, P<0.0001) in anti-CD20 resistant cells compared with 100% in sensitive cells. In contrast, use of the hyperpolarizing ivermectin resulted in mimicking anti-CD20 resistant upregulation of BTK and anti-CD20 sensitive cells intolerant to decreased calcium levels.
Conclusions: RR and OR NHL cells were associated with downregulation of immune signaling pathways, cytokine hyposecretion, and upregulation of BCR signaling. Furthermore, these observed biological changes were associated with decreased intracellular calcium suggesting its role as a master regulator in anti-CD20 resistance. Utilizing depolarizing and hyperpolarizing pharmacologic agents, we were able to restore favorable signaling changes associated with anti-CD20 antibody sensitivity as well as mimic a resistant phenotype in sensitive cells. Additional investigation of the modulation of calcium signaling as a novel mechanism and target for the treatment of anti-CD20 resistant NHL is warranted.
Evens:Pharmacyclics International DMC: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Affimed: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Acerta: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Consultancy; Tesaro: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.